
The small dips in the general trend across the period are caused by the sub-orbitals.This is due to the distance from the nucleus and the shielding by the inner shell electrons. Ionization energies decrease down a group.


The ionic radii increase as you move down a Group due to increasing energy levels.As you move across a period the ionic radii decrease with a jump between positive and negative ions.Increasing electron repulsion also causes the radius to increase. Negative ions ( anions) have larger atomic radii than their parent atoms because they have gained electrons.Positive ions ( cations) have smaller atomic radii than their parent atoms because they have lost electrons.Ionic radius is the atomic radius of an ion in ionic crystal structures. Which property generally decreases across period 3? The atomic radius decreases across a Period because the effective nuclear charge increases which increase the attraction of the nucleus and the outer shell electrons.The atomic radius increases as you go down a Group because you are adding energy levels.As you go from left to right, the effective nuclear charge increases because as you are adding protons, you are still in the same energy level so the inner electrons are not increasing.The atomic radius is not how big the atom is but is measured as half the distance between neighbouring nuclei.Properties of elements and their trends Just a note that all the trends are written about in here are in the data booklet provided in the exams but you will still need to know why these trends happen. Relatively stable metals with only moderate reactivity – useful for construction.
#DIFFERENT BLOCKS IN PERIODIC TABLE FULL#
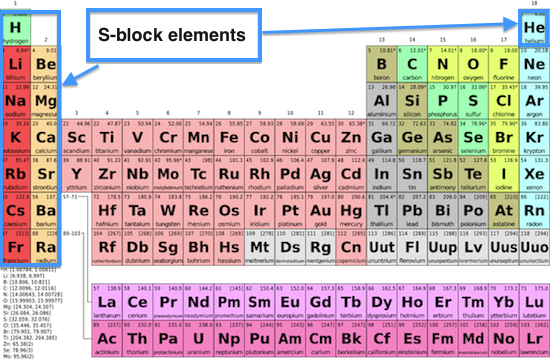
The d-block region (This excludes zinc and the elements below it as they have a full d subshell) Reactive metals – but less reactive than group 1. The most reactive group of metals – react strongly with cold water ( Videos). Period: number of occupied (electron) shells Names of special groups with characteristic properties Group Name (a) Distinguish between the terms group and period in terms of electron arrangement.Ī: (2 Marks) Group: number of outershell/valence electrons The key take away is, that just by looking at where an element is positioned you can immediately know what it's configuration is.Ĭarbon and silicon belong to the same group of the periodic table. The diagram above shows you how the sp,p,d,f blocks are organized. So it's highest sub level in its electron configuration is P and it is filled with three electrons. E.g Phosphorus is in the third element in the P block.The position within the block tells you the number of electrons int he orbital These blocks represent the highest sublevel occupied by the elements within these blocks. The four needed for IB are the s,p,d,f blocks. The periodic table is separated into different blocks. The periodic table and electron configuration These different types of elements are found in different regions of the periodic table. The periodic table can be classified as non-metals, metals and metalloids.Elements in the same group have the same number of outer electrons and have similar chemical properties.The period number ( n) is the outer energy level that is occupied by electrons.The elements are ordered by increasing atomic number.Groups: Vertical columns of the periodic table Periodic table basics Periods: Horizontal rows of the periodic table


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
